Grinding processes are fundamental in various industries, serving as the backbone of manufacturing and materials processing. The choice between wet and dry grinding methods holds significant importance, as it can profoundly impact efficiency, product quality, and environmental considerations. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the nuances of wet and dry grinding, outlining their respective advantages and disadvantages. By the end of this article, you will be well-equipped to make an informed decision based on your specific needs and circumstances.
Understanding Wet Grinding
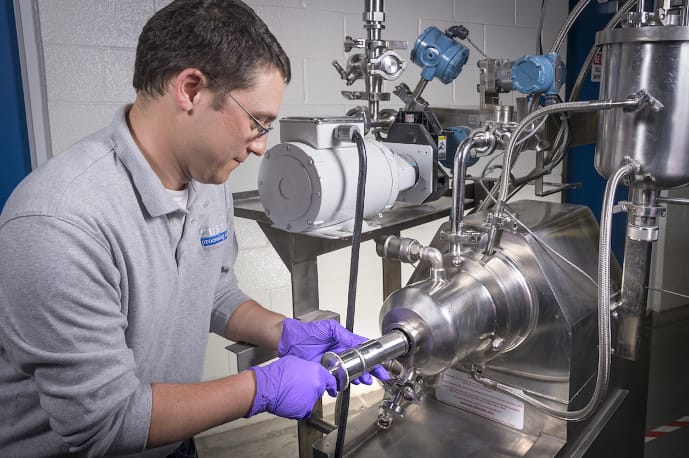

Wet grinding is a machining process that involves using a liquid, typically water or a specialized coolant, to aid in abrasive material removal. The workpiece and abrasive wheel are constantly lubricated during the process, reducing friction and heat generation. This method is widely employed in various industries, including the automotive, ceramics, and food processing sectors. Bead milling machines, like at All Win Machinery, play a crucial role in achieving the desired results in these processes.
The benefits of wet grinding are manifold. Firstly, it results in reduced dust generation, promoting a cleaner working environment. This not only enhances the safety and health of workers but also prevents the contamination of the workspace. Additionally, the cooling effect of the liquid helps prevent heat-induced damage to both the workpiece and the grinding wheel. This is particularly critical when dealing with materials that are sensitive to temperature changes or require high precision. Furthermore, wet grinding often leads to superior workpiece surface quality, making it a preferred choice for precision applications where surface finish matters.
In industries where precision and quality are paramount, wet grinding shines. For instance, in the manufacturing of advanced ceramics, where the slightest imperfection can compromise the final product, it is indispensable. The constant flow of coolant ensures that the temperature remains within a narrow, controlled range, preventing cracks and ensuring uniform material removal.
Exploring Dry Grinding
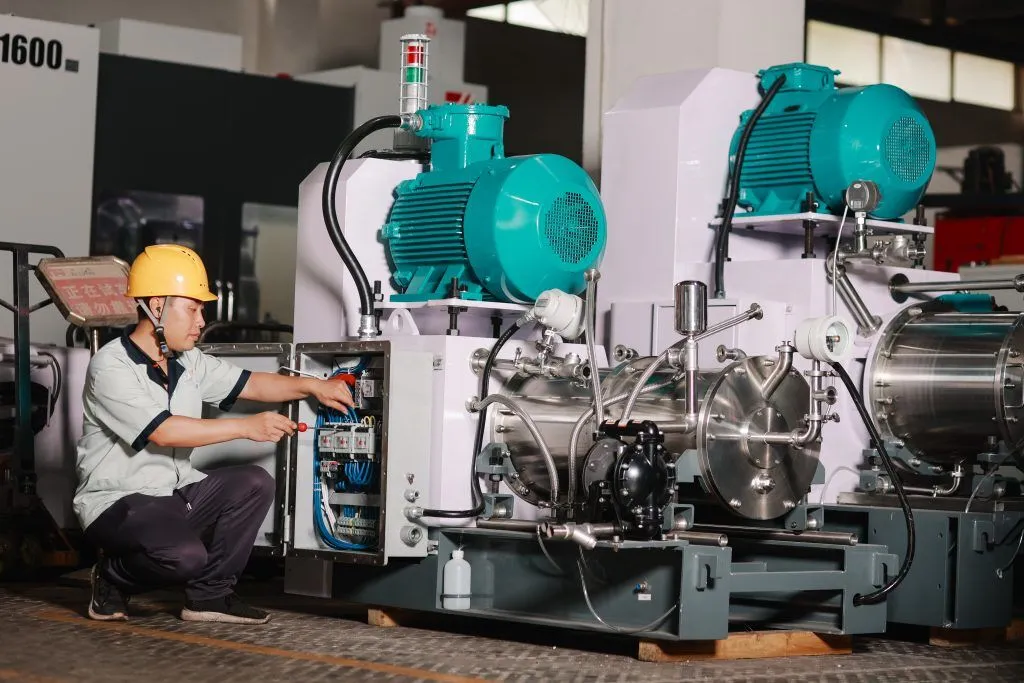
In contrast, it involves abrasive material removal without the use of a liquid coolant. Instead, the process relies on efficient heat removal through ventilation and cooling mechanisms. Dry grinding is favored in industries where rapid material removal is essential, such as metalworking, construction, and woodworking.
It offers its own set of advantages, which cater to the demands of these industries. It typically consumes less energy compared to wet grinding, which can translate into substantial cost savings, especially in high-volume production settings. Moreover, it enables faster material removal rates, thereby increasing productivity. The versatility of dry grinding makes it suitable for a wide range of materials and applications, from shaping metal components to preparing surfaces for painting or coating.
Key Considerations for Choosing Between Wet and Dry Grinding

The decision is multifaceted and depends on several crucial factors. Material type, workpiece size, and desired finish are paramount considerations. Materials that are prone to heat damage, like ceramics and certain composites, often benefit from wet grinding, whereas metals and some plastics may fare better with dry one.
Real-world examples and case studies can illuminate the decision-making process. For instance, in the aerospace industry, precision components may require wet grinding to achieve the required surface finish, while dry grinding may be preferred for bulk material removal during initial shaping. In scenarios where both precision and efficiency are vital, a combination of wet and dry processes may be employed at different stages of the manufacturing process to optimize results.
It’s crucial to consider workpiece size when choosing between wet and dry technologies. For smaller parts or intricate components where precision is essential, wet grinding’s cooling effect and control over temperature make it the preferred choice.
Furthermore, the desired finish plays a pivotal role. If achieving a smooth, polished surface is the primary goal, wet grinding’s ability to minimize surface imperfections shines.
Environmental and Safety Concerns

Environmental and safety considerations are critical when choosing between wet and dry grinding. Each method presents its own set of challenges and solutions.
Wet grinding consumes water, potentially raising concerns about water usage and waste generation. To mitigate these environmental impacts, industries have implemented various practices and technologies. Water filtration and recycling systems can be employed to minimize water consumption and reduce the discharge of wastewater into the environment. Additionally, the use of eco-friendly coolants can further lessen the environmental footprint of wet grinding.
Safety considerations are paramount, especially when dealing with potentially hazardous materials. Dry technology, in particular, presents a risk of dust explosions, especially when working with combustible materials like certain metals or organic substances.
The Clear Choice: Wet Grinding Reigns Supreme
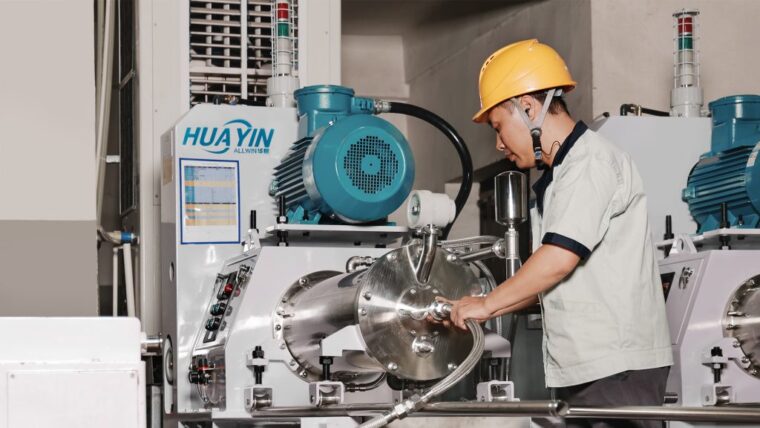

When it comes to choosing between wet and dry grinding, the answer becomes abundantly clear – wet grinding is the superior choice for a multitude of reasons.
- Precision and Workpiece Quality: It stands tall as the champion of precision and workpiece quality. Its use of liquid coolant ensures that workpieces maintain their desired finish, meeting stringent quality standards. Whether you’re in the aerospace industry crafting precision components or the ceramics industry demanding flawless surfaces, wet grinding delivers results that dry technology simply cannot match.
- Environmental and Safety Benefits: It embodies environmental responsibility and safety. It virtually eradicates the issue of dust, which plagues dry grinding operations and poses health hazards for workers. By keeping the workspace clean and dust-free, it also eliminates the risk of dust explosions. Furthermore, wet systems can be designed to minimize water usage and promote responsible waste management, aligning with sustainability goals.
- Technological Advancements: It continues to evolve with the integration of cutting-edge technologies. Innovations in bead milling machines and eco-friendly coolants have elevated wet grinding to new heights. Bead milling machines are becoming smarter, more precise, and efficient, further solidifying wet grinding’s position at the forefront of the processes.
- Versatility and Wide Applications: It offers versatility that spans across a myriad of materials and industries. Whether you’re shaping metals in automotive manufacturing or perfecting ceramic components in advanced technology, wet grinding adapts to your needs. Its ability to excel in diverse applications makes it a dependable choice for many.
In conclusion, the choice between wet and dry grinding is not a one-size-fits-all decision but a multifaceted one.
To make the right choice, consider the material, workpiece size, desired finish, and environmental and safety concerns. By carefully assessing these factors, you can optimize your processes and achieve the best results for your unique needs.
This comprehensive guide has delved into the intricacies of wet and dry grinding, providing insights into their advantages, disadvantages, and real-world applications. As industries continue to evolve and sustainability becomes increasingly important, the choice between wet and dry grinding will continue to be influenced by technological advancements and environmental considerations. Ultimately, it’s crucial to approach the decision with a holistic view, carefully balancing precision, efficiency, safety, and sustainability to achieve the best outcomes for your specific requirements.
